How is Electricity Generated, Transmitted and Distributed?
Learn How is Electricity Generated, Transmitted and Distribute.
Electricity generation, transmission and distribution is a complex engineering process. The process requires huge investment and skilled manpower. The basics of generating electricity remains the same in all forms of electricity such as hydroelectricity, electricity generated using coal, nuclear electricity, renewable energy sources etc. Let us understand in detail.
Table of Contents:
How is Electricity Generated?
Electricity is generated or produced by turning or rotation of turbines. These turbines can be rotated by any means – coal, steam, nuclear energy, renewable energy such as solar energy etc. In most power plants, turbines are rotated by the pressure of steam. This steam is created by boiling water using burning coal in large boilers. The pressure of steam is such that is turns the turbines, which in turn generates electricity.
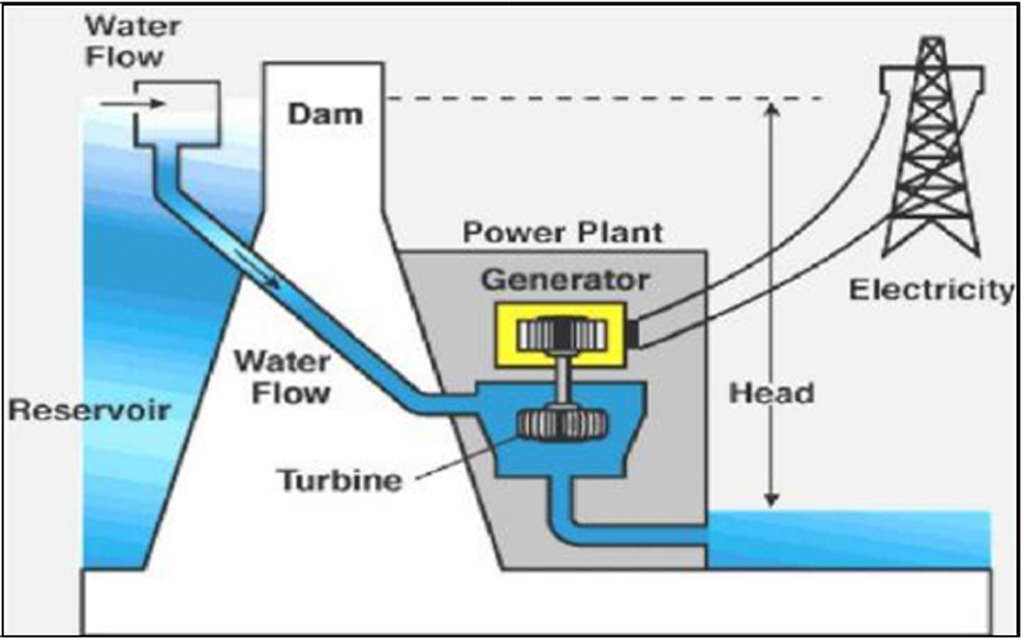
Hydroelectricity uses the force of running water downstream a man-made water reservoir dam. The great force of the running water turns the turbines. The motive is to turn the turbines by any means.
How is Electricity Transmitted?
After electricity is generated in power plant, it is time for transmission. This is done by using step-up transformers that increases the voltage. This high voltage electricity is transmitted through a network of electrically conductive wires of aluminum or copper. These lines are called high-voltage transmission lines that can transmit electricity over long distances.
How is Electricity Distributed?
Electricity is distributed via electric distribution substation. At the substation, the high voltage electricity from the high-voltage transmission lines is passed through step-down transformers that lower the voltage. The electricity is then transmitted to network of local electric distribution lines. Before electricity enters a home, the voltage is again lowered using step-down transformers. In most countries the voltage is 220 V AC or 110 V DC. In a home, electricity is distributed to different outlets by network of wires through electrical wiring.
Related Articles:
- Types of Electric Current
- How to Convert AC to DC using Diode
- Types of Electric Circuit
- How Electronic / Electrical Circuit Works
- How to Reduce Electricity Bill
- Solar Energy – Definition, Uses, Advantages, Facts
- Different Types of Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
- Top 5 Green Hydrogen Energy Companies in India Listed in Stock Market








Thank you sharing such good information.I had one suggestion for Power Distirbution projects
Detailed necessarily supply. kaushik Roy Mie and M.Tech and energy auditor by BEE WBLCB certified electrical safety
very good and educational information thank you so much, keep up the good work


Well said